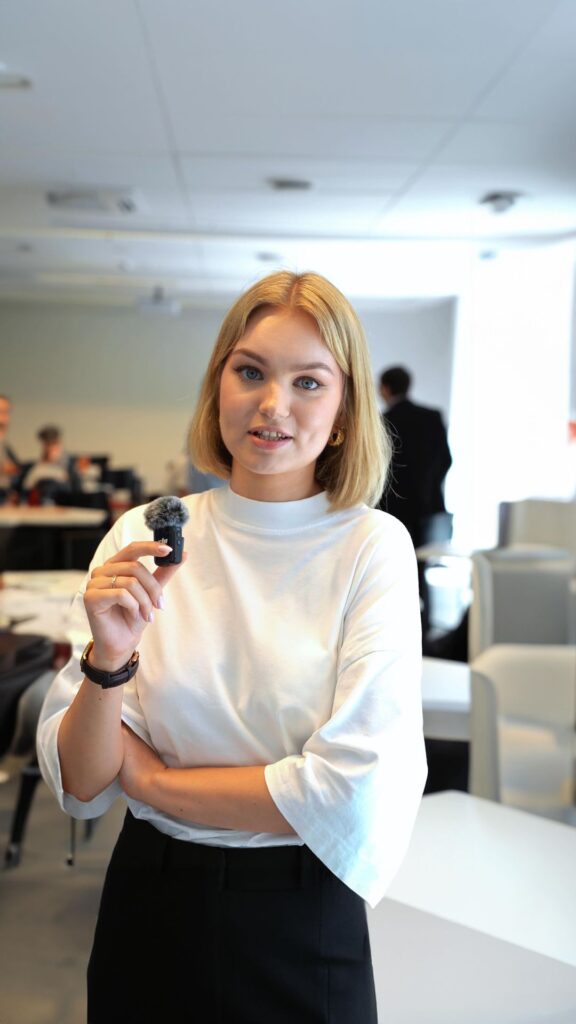
Ekonomika ir politika
Dėstytojai iš garsiausių Amerikos ir Europos universitetų padės tau suprasti, kokią įtaką viena kitai daro ekonomika, politika ir verslas. Po mokslų tavęs lauks analitiko, vadovo, politiko arba mokslininko karjera.

Susipažink su studijų programa iš arčiau








Programos struktūra
Ką išmoksiu?
Ką išmoksiu?
Ką išmoksiu?
Ką išmoksiu?
Ką išmoksiu?
Ką išmoksiu?
Ką išmoksiu?
Kuo galėsiu būti?
Diplomatu
Tarptautinių santykių specialistu
Politiku
Ekonomistu
Strategu
Vadybos konsultantu
Europos sąjungos institucijų projektų vadovu

Programos išskirtinumai
Galimybės užsienyje

Dvigubas diplomas su BI Norwegian Business School
Studijos Norvegijoje, viename iš 1 procento pasaulio universitetų, turinčių “Triple Crown” akreditaciją (AMBA, EQUIS, AACSB)Kaip tai vyksta? Ketvirtame studijų semestre vyksta atranka. Studentai, praėję atranką vienerius metus mokysis BI Norwegian Business School.
Kiek tai kainuoja? Studijų BI Norwegian Business School metu yra mokamas šios mokymo įstaigos studijų mokestis. Pritaikoma dešimties procentų nuolaida. ISM universitetui mokėti už studijas tą semestrą nereikia.
Kur aš gyvensiu studijuodamas Norvegijoje? BI Norwegian Business School siūlo įvairaus tipo apgyvendinimą studentų rezidencijose.
Kokią naudą aš gausiu? Beveik per tą patį laiką gausi dviejų aukštųjų mokyklų diplomus. Formuosi tarptautinį savo pažinčių ratą. Mokydamasis užsienio šalyje praplėsi savo akiratį ir gebėsi laisvai orientuotis bei dirbti multikultūrinėje aplinkoje.
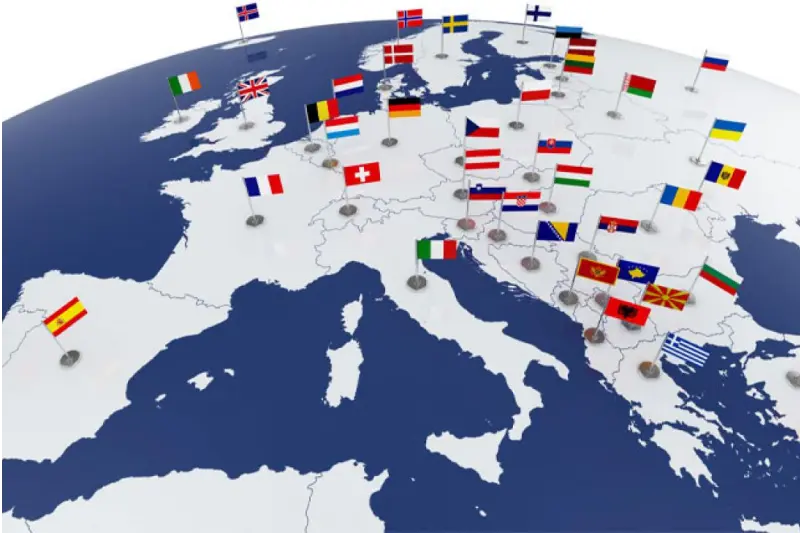
100+ universitetų mainų partnerių visame pasaulyje
Mainų galimybės įvairiuose pasaulio universitetuose iš kurių trečdalis turi bent vieną prestižinę verslo universitetų akreditaciją (AACSB, EQUIS, AMBA)Kaip tai vyksta? Kiekvieną semestrą gali rinktis universitetą, kuris yra ISM partneris ir dalyvauji atrankoje. Sėkmingai praėjus atranką, kitą semestrą išvyksti į mainų programą.
Kiek tai kainuoja? Tai nieko papildomai nekainuoja. Moki įprastą studijų kainą.
Kiek laiko trunka? Mainų semestras trunka apie 5 mėnesius
Ką turiu padaryti, norėdamas dalyvauti mainų programoje? Turi mokytis taip, kad neturėtum daugiau nei vienos skolos.
Naujienos ir renginiai
Studijuodama ISM sutikau daug asmenybių, kurios nuolat įkvepia savo tobulėjimu.

Studijos ISM - prieinamos kiekvienam
Kainos, finansavimas ir priėmimas
Investicijos į studijas atsiperka
Finansavimo galimybės
D.U.K.
Kokiais etapais vyksta priėmimas į ISM universitetą?
Kuo ypatingas išankstinis priėmimas ir kodėl turėčiau stoti per jį?
Kokius egzaminus turiu išlaikyti, norint įstoti į ISM?
Kas yra Valstybės studijų stipendija (vnf/st)? Ką turiu daryti, jog ją gaučiau?
Mokyklą baigiau užsienyje. Ar galiu stoti į ISM?
Ar galiu įstoti į ISM, jei jau studijavau kitame universitete?
Kokios yra ISM universiteto praktikos galimybės?
Kokia kalba vyks paskaitos ISM universitete?
Ar galima stoti į išlyginamąsias studijas po kolegijos?
Kitos bakalauro studijų programos
Svarstai apie bakalauro studijas?